5G and Beyond
The advent of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of wireless communication, promising unprecedented speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive connectivity. As we look to the future, 5G is just the beginning. At SparkScribe Technologies, we are at the forefront of leveraging these advancements to drive innovation and growth. In this blog post, we’ll explore the capabilities of 5G, its potential applications, and the future of connectivity beyond 5G
The advent of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of wireless communication, promising unprecedented speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive connectivity. As we look to the future, 5G is just the beginning. At SparkScribe Technologies, we are at the forefront of leveraging these advancements to drive innovation and growth. In this blog post, we’ll explore the capabilities of 5G, its potential applications, and the future of connectivity beyond 5G.
Understanding 5G Technology
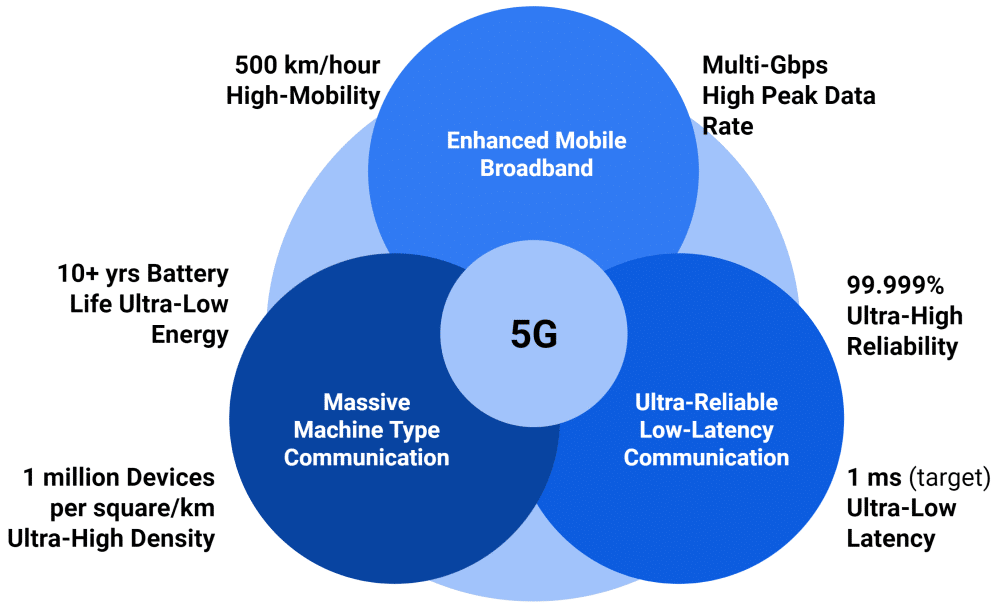
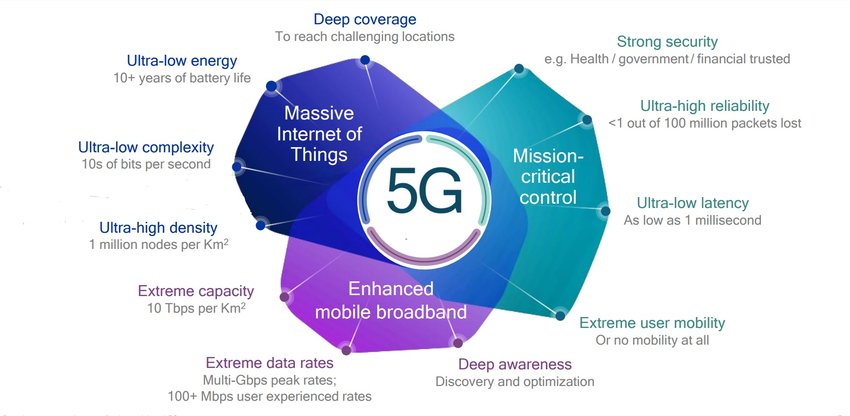
5G, the fifth generation of mobile networks, offers significant improvements over its predecessors. It operates on three key frequency bands: low-band, mid-band, and high-band (millimeter wave), each with its unique advantages.
Key Features of 5G:
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Provides faster data speeds and greater capacity, enabling high-quality video streaming and immersive experiences.
- Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC): Ensures near-instantaneous communication, crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles and remote surgery.
- Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC): Supports the connection of a vast number of IoT devices, paving the way for smart cities and industrial automation.
Potential Applications of 5G
1. Smart Cities
5G enables the deployment of smart city infrastructure, including intelligent traffic management, energy-efficient buildings, and enhanced public safety systems.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
With ultra-low latency and high reliability, 5G facilitates real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure, enhancing the safety and efficiency of autonomous driving.
3. Healthcare
5G supports telemedicine, remote surgery, and real-time monitoring of patients, revolutionizing healthcare delivery and access.
4. Industrial Automation
5G empowers Industry 4.0 by enabling the seamless integration of robotics, AI, and IoT devices in manufacturing and logistics, increasing productivity and reducing downtime.
5. Entertainment and Media
5G enhances augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and 4K/8K video streaming experiences, transforming the way we consume and interact with media.
The Future Beyond 5G: 6G and Next-Generation Technologies
While 5G is still in its rollout phase, research and development are already underway for 6G, the sixth generation of mobile networks, which is expected to be commercially available by 2030.
Key Innovations in 6G:
1. Terahertz Frequencies
6G will utilize terahertz (THz) frequencies, offering even higher data rates and capacity, enabling advanced applications like holographic communication and immersive VR.
2. AI and Machine Learning Integration
6G will heavily integrate AI and machine learning to optimize network performance, manage resources efficiently, and enable self-healing networks.
3. Enhanced Connectivity
6G aims to provide seamless connectivity across land, sea, air, and space, ensuring ubiquitous coverage and reliable communication everywhere.
4. Quantum Communication
Quantum communication technologies will enhance the security and speed of data transmission, paving the way for ultra-secure and high-capacity networks.
5. Sustainable Networking
6G will focus on energy efficiency and sustainability, developing green communication technologies to reduce the environmental impact of global connectivity.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Infrastructure Development
Building the infrastructure for 5G and beyond requires significant investment in new base stations, fiber-optic networks, and edge computing facilities.
2. Security and Privacy
With increased connectivity comes heightened security and privacy risks. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and data protection protocols is paramount.
3. Spectrum Allocation
Allocating sufficient spectrum for 5G and future networks involves regulatory challenges and international coordination to avoid interference and ensure global compatibility.
4. Device Compatibility
Ensuring that new devices are compatible with evolving network standards is essential for seamless user experiences and widespread adoption.
5. Environmental Impact
Balancing the expansion of connectivity with environmental sustainability involves developing energy-efficient technologies and minimizing electronic waste.
Conclusion
The transition to 5G marks a transformative era in connectivity, with far-reaching implications across various sectors. As we look to the future, technologies beyond 5G promise even greater advancements, from terahertz communication to AI-driven networks. At SparkScribe Technologies, we are dedicated to harnessing these innovations to deliver cutting-edge solutions and drive the next wave of digital transformation. Stay tuned to our blog for more insights and updates on the future of connectivity.